Hreflang Checker
Audit the hreflang implementation of your WordPress site

A feature of the Hreflang Manager plugin for WordPress
Audit the hreflang implementation of your WordPress site

A feature of the Hreflang Manager plugin for WordPress
The Hreflang Checker included in Hreflang Manager automatically audits your hreflang implementation and detects the most common and critical configuration errors. The audit runs directly from the plugin back end and can be performed across all sites in your network.
A correct hreflang implementation is essential for international SEO, but even small configuration mistakes can cause search engines to ignore your hreflang tags entirely.
The Hreflang Checker included in Hreflang Manager allows you to validate your setup proactively, without waiting weeks for issues to appear in search engine monitoring tools. By running audits directly on your server, the checker has no practical limits on the number of pages it can analyze and can verify hreflang annotations across all language or region targeted sites in your network.
Instead of testing individual URLs with external tools, you can perform a complete, centralized audit and immediately identify issues that may affect indexing, visibility, or international targeting.
This check verifies that every URL referenced in your hreflang tags is reachable and returns a valid 200 (OK) HTTP response.
If a hreflang URL returns status codes such as 404, 301, 302, or 500, search engines may ignore the associated hreflang annotations. This can result in incorrect language or regional pages being shown in search results.
By identifying invalid HTTP responses, the checker helps ensure that all hreflang URLs are accessible, indexable, and eligible for proper international targeting.
Multiple hreflang tags targeting the same language, script, or region on a single page can introduce ambiguity.
Duplicate entries may cause search engines to disregard your hreflang configuration or apply it inconsistently. This validation detects duplicated hreflang annotations so you can keep your implementation clean, unambiguous, and easier for search engines to interpret.
This check ensures that each page includes a self-referencing hreflang tag.
A self-referencing hreflang explicitly signals that the current page is the correct version for its own language, script, or region. Without it, the hreflang cluster may be considered incomplete or unreliable.
Detecting missing self-references helps reinforce consistency and improves the overall reliability of your international setup.
Hreflang values must follow strict ISO standards to be recognized by search engines.
Invalid language, script, or region codes can cause hreflang annotations to be ignored entirely. This validation identifies incorrect or non-compliant codes, allowing you to align your hreflang tags with accepted standards and ensure they are processed correctly.
For international setups that serve users outside defined language or regional targets, the x-default hreflang tag plays an important role.
It indicates which page should be shown when no specific hreflang match applies. When this annotation is missing, search engines may lack a clear fallback option. This check detects the absence of the x-default tag, helping you define a proper default experience for unsupported languages or regions.
Hreflang annotations must be bidirectional to be valid.
If a page references an alternate version, the referenced page must link back using a corresponding hreflang tag. Missing return links break this relationship and can invalidate the entire hreflang cluster.
This validation identifies incomplete hreflang linking so you can restore full two-way connections between pages.
Canonical tags and hreflang annotations must work together.
When a page declares a canonical URL that conflicts with its hreflang tags, search engines receive mixed signals. This can result in incorrect indexing or the wrong version being displayed in search results.
By detecting canonical–hreflang conflicts, the checker helps ensure consistent international targeting and prevents unintended SEO issues.
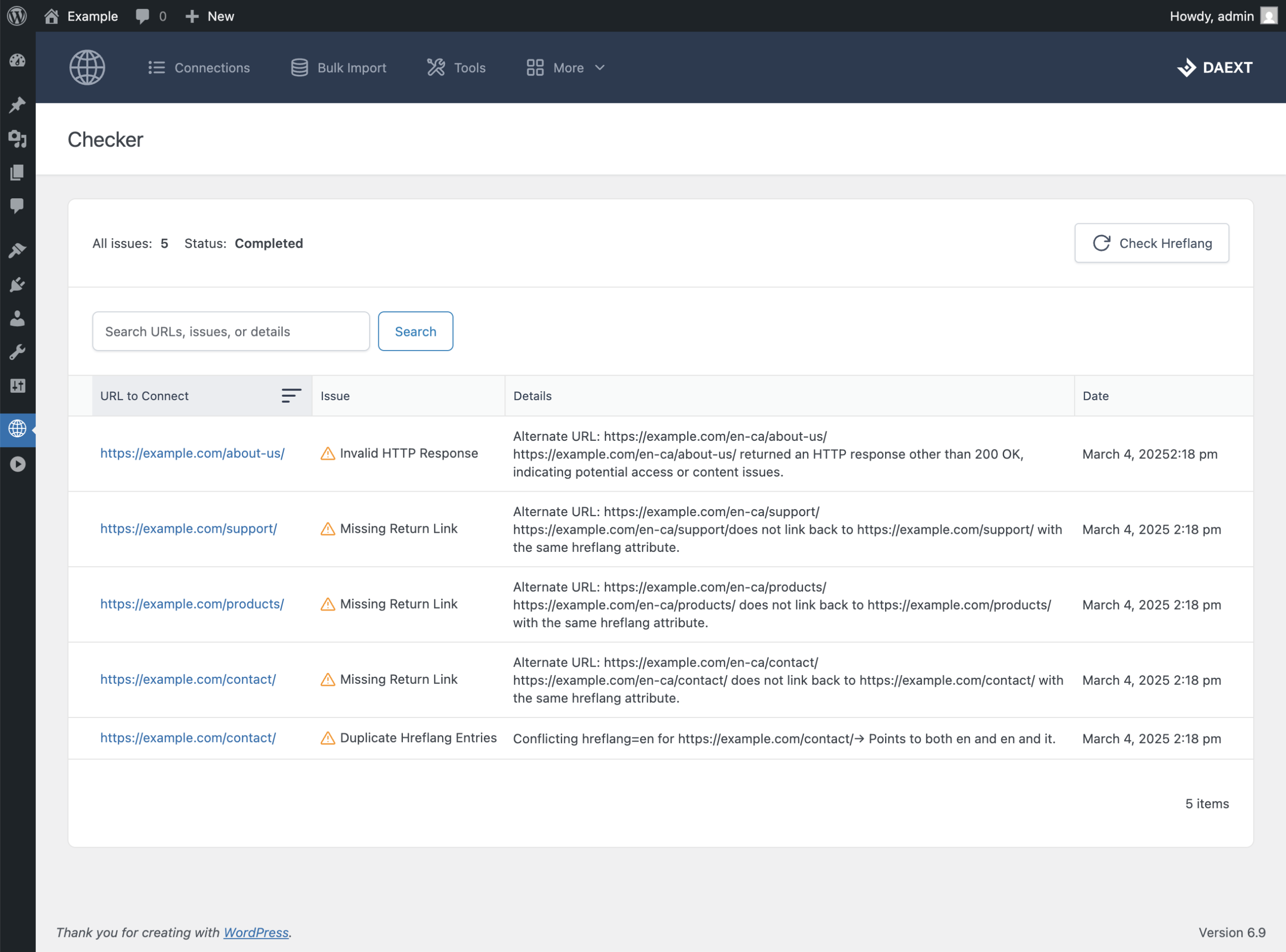
The Pro version of Hreflang Manager includes an additional “Checker” menu in the plugin back end. From there, you can start an audit by clicking the “Check Hreflang” button.
The checker analyzes all URLs across your site, or network, and reports any detected issues in a structured table. Each report entry includes the affected hreflang item, a description of the issue, helpful details for resolving it, and the date the problem was first detected.
The checker uses your own server resources to perform the audit. Timing and execution settings can be configured from the plugin options to ensure the process is compatible with your hosting environment and the size of your site.